Cell Based Assays
3D Spheroid & Organoid System
- ❯ Generation of 3D cancer spheroids and organoids
- ❯ Drug screening and drug toxicity assays
- ❯ Whole spheroids/ organoids staining & imaging
Cell Viability Assays
- ❯ MTT/MTS assays: Measure cell metabolic activity through the reduction of tetrazolium compounds.
- ❯ CellTiter-Glo®: It is a cell assay that measures cell viability by quantifying ATP released from living cells, providing a direct indication of the number of viable cells in a culture.
- ❯ Resazurin reduction assay (Alamar Blue): Detect metabolic activity through resazurin reduction.
Cytotoxicity Assays
- ❯ Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay: Detects cell membrane damage by measuring LDH release.
- ❯ Trypan blue exclusion assay: Counts viable cells that exclude the dye.
- ❯ Propidium iodide staining: Identifies dead cells by staining DNA.
Apoptosis Assays
- ❯ Caspase 3/7 Assay: Measures the activation of 3/7 caspases which are key enzymes that execute apoptosis, or programmed cell death in cells.
- ❯ Annexin V staining: Detects phosphatidylserine exposure on the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane.
- ❯ TUNEL assay (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling): Identifies DNA fragmentation.
Proliferation Assays
- ❯ BrdU (Bromodeoxyuridine) incorporation assay: Measures DNA synthesis by incorporating BrdU into newly synthesized DNA.
- ❯ Ki-67 staining: Detects the proliferation marker Ki-67 in cells.
- ❯ EdU (5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine) incorporation assay: A more modern alternative to BrdU.
- ❯ Cell cycle analysis: Cell cycle analysis by DNA content measurement is commonly performed using flow cytometry with fluorescent dyes like propidium iodide or DAPI. The fluorescence intensity correlates with the amount of DNA in cells, allowing differentiation of cells in different phases of the cell cycle.
Signal Transduction Assays
- ❯ Calcium flux assays: Measure intracellular calcium levels using fluorescent indicators.
- ❯ cAMP assays: Quantify cyclic AMP levels as a marker of GPCR activation.
- ❯ Phosphorylation assays: Detect the phosphorylation status of proteins using antibodies.
Selecting Fashion Theme
- ❯ Luminex assays: Simultaneously measure multiple analytes in a single sample using bead-based technology.
- ❯ Cytokine profiling: Quantify multiple cytokines secreted by cells.
Enzymatic Assays
- ❯ Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): The fluorescent dyes like DCFDA that react with ROS to produce a fluorescent signal is used. The cells are incubated with the probe, stimulated to produce ROS, and the fluorescence is measured.
- ❯ Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS): The NOS assay is crucial in understanding various biological processes, such as neurotransmission, vascular regulation, immune response, and apoptosis, where NO plays a significant role. The assay involves a series of reactions that convert NO into nitrite and nitrate, which are then quantified using colorimetric or spectrophotometric methods.
Cell Migration & Invasion Assays
- ❯ Scratch (wound healing) assay: Measures cell migration into a scratched area on a cell monolayer.
- ❯ Migration assay: Assesses the movement of cells through a membrane towards a chemoattractant.
- ❯ Matrigel invasion assay: Evaluates cell invasion through a Matrigel-coated membrane.
High-Content Screening (HCS)
- ❯ Automated microscopy: Captures and analyses multiple cellular parameters.
- ❯ Image-based assays: Quantify cellular features such as morphology, protein localization, and cell cycle.
Cell Differentiation Assays
- ❯ Osteogenesis, adipogenesis, and myogenesis assays: Measure the differentiation of stem cells into specific lineages.
- ❯ Neurite outgrowth assays: Assess the differentiation and growth of neurons.
Permeability Assays
- ❯ CaCO2: It is a gold standard method for evaluating both passive and active transport and absorption of orally administered drugs, making it an indispensable tool in drug development
- ❯ Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA): It is a complementary tool to evaluate the passive transportation of drugs.
Receptor Internalization & Trafficking
- ❯ Fluorescent ligand binding: Visualize receptor internalization using labelled ligands.
- ❯ Tag-based assays (e.g., HA, GFP-tagged receptors): Monitor receptor trafficking.
In Vitro ADME
- Solubility : Kinetic, Equilibrium
- Plasma Protein Binding : Mouse, Rat, Dog, Human
- Permeability : PAMPA, Caco2 (Unidirectional, Bidirectional)
- Microsomal Metabolic Stability : Mouse, Rat, Dog, Human
- Human CYP450 assays : Inhibition, Isoform Phenotyping
- Cytotoxicity : HepG2, A549, MDCK cell lines
- MET-ID

Biochemical Assays

Enzyme Activity Assays
- > Substrate-based assays
- > Coupled enzyme assays
- > Reporter enzyme assays

Binding Assays
- > Radioligand binding assays
- > Fluorescence polarization (FP)
- > Surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
- > Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC)
Protein-Protein Interaction
- > Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
- > Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H)
- > Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET)
- > Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)

Cell-based Assays
- > Reporter gene assays
- > Cell viability assays
- > Apoptosis assays
- > High-content screening (HCS)
Receptor Binding Assays
- > GPCR (G-protein-coupled receptor) assays
- > Ion channel assays

Nucleic Acid Assays
- > Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
- > RNA interference (RNAi) assays
- > CRISPR/Cas9-based assays

Post-translational Modifications
- > Kinase assays
- > Ubiquitination assays
- > Methylation and acetylation assays

Metabolic Assays
- > Metabolite profiling
- > Oxygen consumption rate (OCR)
- > Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR)

Spectroscopic Assays
- > UV-Vis spectroscopy
- > Mass spectrometry
- > Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
IPSC Platform
Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology has emerged as a state-of-the-art tool in drug discovery, integrating molecular biology, genetics, and cellular physiology to advance the modelling human diseases and discovering new treatments. Unlike animal models, iPSCs can differentiate into various cellular subtypes, allowing for the creation of more accurate disease models. This technology enables researchers to conduct mechanistic studies, screen for new drugs, and identify targets of interest. Our expertise in iPSC technology offers tailored solutions for generating iPSC clones suitable for cellular assays and screening, characterization, differentiation into multiple lineages, genome editing using CRISPR, disease modelling, disease mechanisms, drug screening for efficacy and toxicity, personalized medicine, biological relevance and in vitro assays using iPSC derivatives. This technology also helps reduce the use of animal models, making it a valuable tool for researchers seeking to accelerate the discovery of new treatments.

Disease Areas


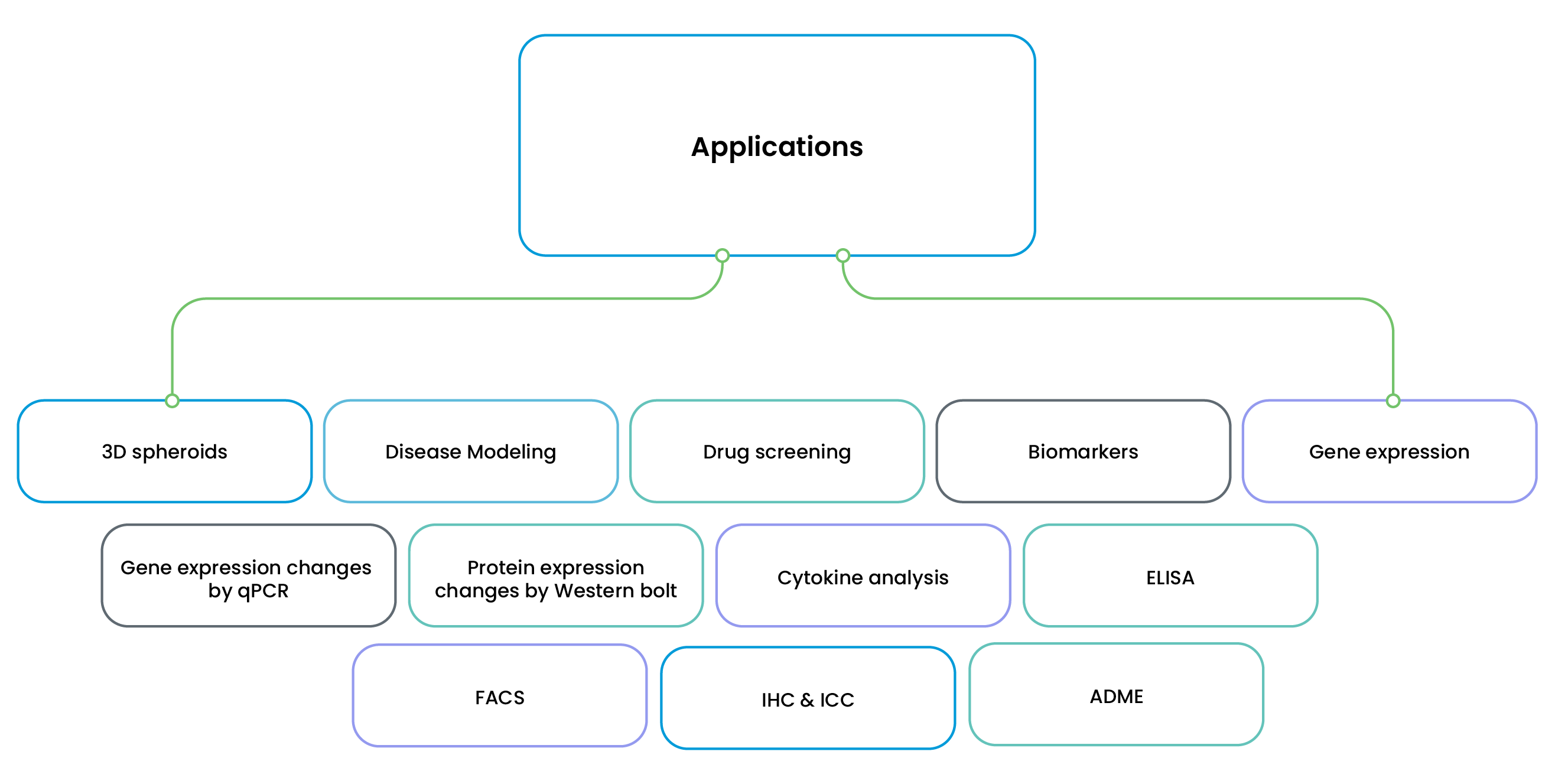


Assay Types
- ❯ Compound Screening
- ❯ Drug Sensitivity & Resistance Assays
- ❯ Cytotoxicity Assays - 2D/3D Organoids
- ❯ Genetic Modifications
- ❯ Viability Assays
- ❯ Apoptosis Assays
- ❯ Drug Resistance Assays
- ❯ Mitochondrial Functions
- ❯ ATP Production
- ❯ Glucose Uptake Assays
- ❯ Oxidative Stress Markers
- ❯ Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzyme Activity
- ❯ Glucose & Lipid Metabolism Assays
- ❯ Drug Metabolism & Toxicity Screening
- ❯ Biomarkers
- ❯ Gene Expression
- ❯ Protein Expression
- ❯ Cytokine Analysis
- ❯ Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- ❯ Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
iPSC Derived Models
- ❯ Hepatocytes
- ❯ Cardiomyocytes
- ❯ Neurons
- ❯ Pancreatic
Readouts
- ❯ Imaging
- ❯ Plate Readers
- ❯ qPCR
- ❯ ELISA
- ❯ Western Blotting
- ❯ Flow Cytometry
Biomarkers

“The use of biomarkers has the potential to facilitate the availability of safer and more effective drug or biotechnology products, to guide dose selection, and to enhance their benefit-risk profile” – FDA ICH E16
The metamorphosis from “one drug fits all” paradigm of drug discovery to personalized medicine is one of the great success stories of modern drug discovery. Biomarkers play a critical role in this transformation.
The goal of biomarker usage in research is to expedite the drug development process to produce drug therapies as efficiently as possible, while maintaining the safety profile. Biomarkers optimise animal testing & improve human risk assessment. We at Oncogenix offer safety, efficacy and surrogate biomarker services.

ONCOLOGY
Signaling Pathways, DNA Damage, Cytotoxicity, Proliferation, Inflammation, Angiogenesis, Metastasis

METABOLIC DISORDERS

INFECTION
Oncogenix Can Customise Biomarker Assays as per Research Needs
Microbiology Assays
In vitro microbiology assays are essential for advancing scientific and medical knowledge, particularly in the fields of infectious disease research and drug development. These assays are pivotal in drug development, enabling researchers to screen potential antimicrobial compounds and assess their efficacy and toxicity before advancing to in vivo studies. Additionally, they facilitate the understanding of microbial resistance mechanisms, aiding in the design of more effective treatment strategies against resistant strains.


Microbiology assays include:
- ❯ Microbial Identification
- ❯ Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (AST)
- ❯ Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
- ❯ Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
- ❯ Killing Kinetics / Time kill assay - Concentration and Time
- ❯ Resistance Profiling - Single Step & Sub-MIC Passages
- ❯ Biofilm assays
- ❯ Mutation frequency
Antifungal assays include:
- ❯ Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
- ❯ Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC)
Virology
Antiviral Assay
In vitro antiviral assays are used to evaluate the efficacy of antiviral compounds against specific viruses within a controlled cell culture environment. In vitro antiviral assays play a pivotal role in the discovery and optimization of new antiviral therapies. Commonly used in vitro assays include plaque reduction assays, TCID50 assays, and MTT assays, each offering different methods to quantify viral activity and cell viability. These assays are crucial in the early stages of drug development, as they help identify promising antiviral candidates before advancing to in vivo studies and clinical trials.
Antiviral in vitro assays include:
- ❯ TCID50 assay
- ❯ EC50/CC50 Assay
- ❯ Plaque assay
- ❯ Hemagglutination inhibition assay
Molecular Biology
Genome editing or genetic engineering:
CRISPR-Cas9 assay:
Gene editing technology, which provides precise modification of DNA sequences within the genome of living organisms. It is used to create complex cell-based assays that mimic disease states, enabling more physiologically relevant drug discovery and target validation.
T7 endonuclease assay:
The T7 endonucuclease assay is used for evaluating the activity and efficiency of site-specific nucleases, such as the CRISPR-Cas9 system.

Ion Channel Assays:
Patch-clamp technique:
Measures ionic currents through individual ion channels.
Fluorescent dye-based assays:
Detect changes in ion concentrations (e.g., calcium, potassium).
Reporter Gene Assays:
Luciferase reporter assay:
Measures luciferase enzyme activity as an indicator of gene expression.
β-galactosidase (LacZ) assay:
Uses the β-galactosidase enzyme as a reporter.
GFP/RFP assay:
Detects fluorescence as a marker for gene expression.

PCR
qPCR/qRT-PCR
ELISA
Western Blot
Immunology Assays
Immunology and Immuno-Oncology:
Cellular immunophenotyping:
Immunophenotyping is performed using flow cytometry. The labelled cells are processed in a flow cytometer, which allows for the rapid and easy phenotyping of each cell according to the presence or absence of a protein combination.
Cytokine analysis:
Cytokine analysis is performed using ELISA. It is crucial for understanding immune responses, inflammation, and various disease states.
Cytokine gene expression:
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) is a sensitive, accurate, and quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression, providing important insights into immune function and disease pathogenesis.